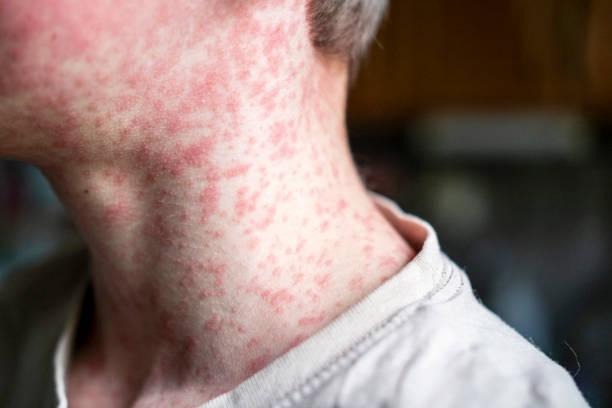
Tips for Treating Redness, Swelling, and Rashes with Skin Creams
Redness, swelling, and rashes of the skin are common dermatological conditions that can happen from numerous causes, such as allergic reactions, irritants, infections, insect bites, autoimmune diseases, or chronic skin conditions like eczema, or psoriasis. Most of these conditions are uncomfortable, and the symptoms can sometimes lead to an inflammatory process, such as disruption of the skin barrier. The management of these conditions often entails identifying the trigger and using topical therapies to decrease discomfort and inflammation.
Topical skin creams are a popular method for treating localised skin conditions. They typically contain ingredients like corticosteroids, antifungals, antibacterials, moisturisers etc. The treatments depend on the condition being treated. This guide is to help understand when and how skin creams might provide some relief from the symptoms of redness, swelling and rashes, along with appropriate skin care.
Common Causes of Redness, Swelling, and Rashes
Before choosing any treatment, it is important to understand the potential causes. The common causes of redness, swelling, and rashes are:
- Allergic Dermatitis – due to fragrances, latex (rare), or other specific ingredients in personal care products.
- Irritant Contact Dermatitis – occurs with repeated contact to harsh soaps, detergents or solvents.
- Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis) – is a chronic skin condition associated with inflammation and severe itching.
- Psoriasis – an autoimmune skin condition that causes red scaly patches on the skin.
- Fungal or Bacterial Infections – localised swelling, redness and/or pain may be caused by a skin infection.
- Heat Rash – occurs from blocked sweat ducts and/or excessive sweating in hot, humid conditions.
Use of Topical Creams and Skin Inflammation
While topical creams may provide symptom relief, the creams may also decrease the local inflammatory response. They can also contribute to repairing the skin barrier and decreasing the risk of further irritation or infection.
An example of a topical preparation for managing inflammatory skin conditions is Panderm Plus cream, which combines antifungal, antibacterial, and corticosteroid agents. It may be used under medical supervision in certain cases of fungal infections with associated inflammation or secondary bacterial infection. Topical corticosteroids like those contained in Panderm Plus may help reduce redness, swelling and pruritis by acting to suppress the inflammation processes within skin.
General Considerations for the Safe use of Skin Creams
Using topical creams correctly is important to make sure creams are effective and to avoid possible side effects. These are some guidelines:
- Speak with a doctor
Correct diagnosis is important. Do not self-diagnose skin rashes, especially if the symptoms continue, worsen, or recurrences are frequent. A dermatologist may prescribe creams specifically depending on the type of rash and the underlying pathology.
- Apply to the Affected Area Only
Only apply creams in a thin film to the inflamed or infected skin unless directed otherwise. Avoid using on open wounds, mucosal surfaces and into the eyes unless the cream is prescribed for these areas.
- Use Clean Hands and Implements
Clean your hands before and after applying the cream. Avoid using applicators or cotton balls to apply unless directed to use, as these can trap bacteria.
- Use as Prescribed
Topical corticosteroids or combination creams should not be used for longer than prescribed without review. If topical treatments are used for a long time, skin thinning, or development of resistance to the active agents (especially if it is an antimicrobial agent), may occur.
- Avoid Triggers and Irritants
You should avoid harsh soaps and/or skin care products that may worsen skin irritation. You should identify and avoid positive environmental or food allergens that may be much more trustworthy in treating flare-ups.
- Moisturising and Barrier Restoration
Skin dryness often worsens symptoms for many inflammatory skin conditions. Daily moisturisation can help both restore and retain the skin’s natural barrier. While this is true for chronic conditions like eczema or psoriasis, use fragrance-free hypo-allergenic emollients or creams, specifically formulated for sensitive skin, if possible.
Some medicated cream treatments can also serve a barrier-restoration purpose, which will help soothe skin and help restore skin integrity, in addition to the active ingredients.
When to Seek Medical Attention
You may have signs or symptoms that indicate you need to seek medical care .
- Rapidly progressing rash, or rash covering a large area
- Fever, or systemic symptoms
- Signs of skin infection, i.e. yellow crusting, substance resembling pus, or increased warmth over the area with the rash
- No improvement in rash after using topical products available over-the-counter
- Rash returns with acute flare-up and/or chronic rash with unknown cause
In these situations, a dermatologist will be able to complete a compartment evaluation, which may include patch testing for allergies, or biopsy-gathering, if required.
Skin Hygiene When Taking Skin Treatment
A significant aspect of managing skin care is skin hygiene:
- You want to bathe or shower for a short amount of time, in lukewarm water.
- You should use mild cleansers devoid of dyes and fragrance.
- You should gently pat the skin dry with a soft towel versus rubbing the area vigorously.
- You should immediately apply creams and/or moisturisers upon washing your skin.
- The Use of Antibacterial or Antifungal Creams
If you are thinking about topical creams that you may use for a secondary infection, skin creams may include a specific agent that targets a particular section of the microbe. Often, these creams are prescribed for:
- Infected eczema
- Fungal infections, i.e. ringworm or athlete’s foot
- Infectious bacterial conditions, i.e. impetigo
Combination creams should be used with care and one should use these in a prescribed fashion. Inappropriate use can lead to resistance to the specific active agent and reinforcements of symptoms in certain conditions.
Using Considerations for Skin Health
The support of skin health is more than topical treatment.
- Ensure you eat a balanced diet, aiming for Vitamin A, C, D, & E; and omega-3 fats.
- Ensure you are drinking plenty of water, which helps with skin elasticity and moisture.
- You want to try and limit any stress-building factors due to the fact that stress is a major contributor to skin illnesses or skin flare-ups—especially in cases of eczema and psoriasis.
- Breathable fabrics (cotton) are recommended to cover areas where a rash may become hot and friction-induced.
Takeaway
The skin may become red, swollen, or rash-like from a variety of distinct conditions ranging from small irritations to more chronic inflammatory conditions. Understanding the cause is half of the battle to treating the problem. Using topical skin cream treatment like Panderm Plus are helpful for localised relief when used for the correct indications, and appropriate for medical staff to provide guidance. General skin care, moisturisers, and directions to avoid skin conditions is equally important.
If you have persistent symptoms or see conditioning worsening, seek medical management. In certain instances, a dermatologist may prescribe other formulations including a product like Clovate GM Cream which pertains to combinations for specific infections or inflammation due to skin issues.